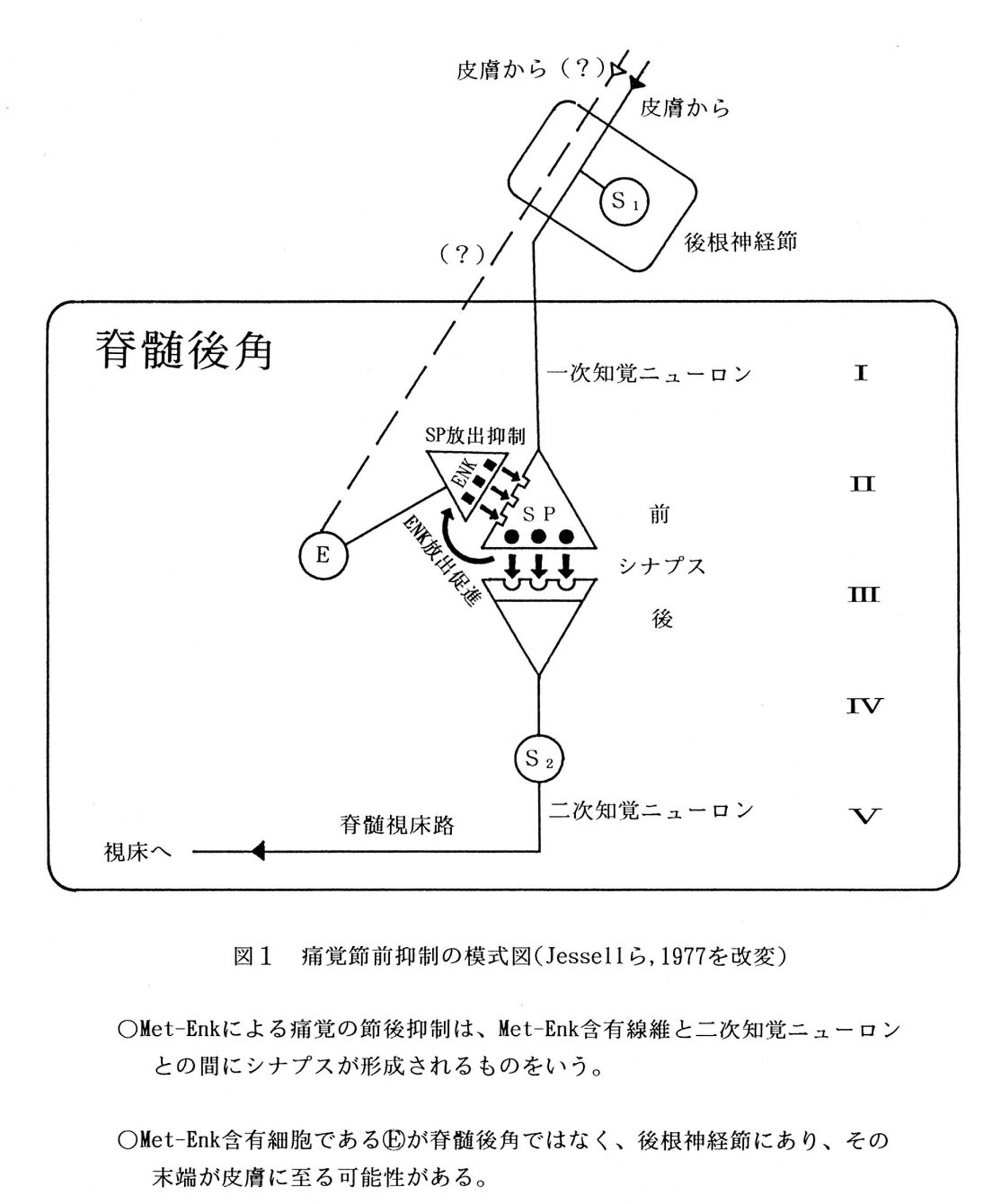
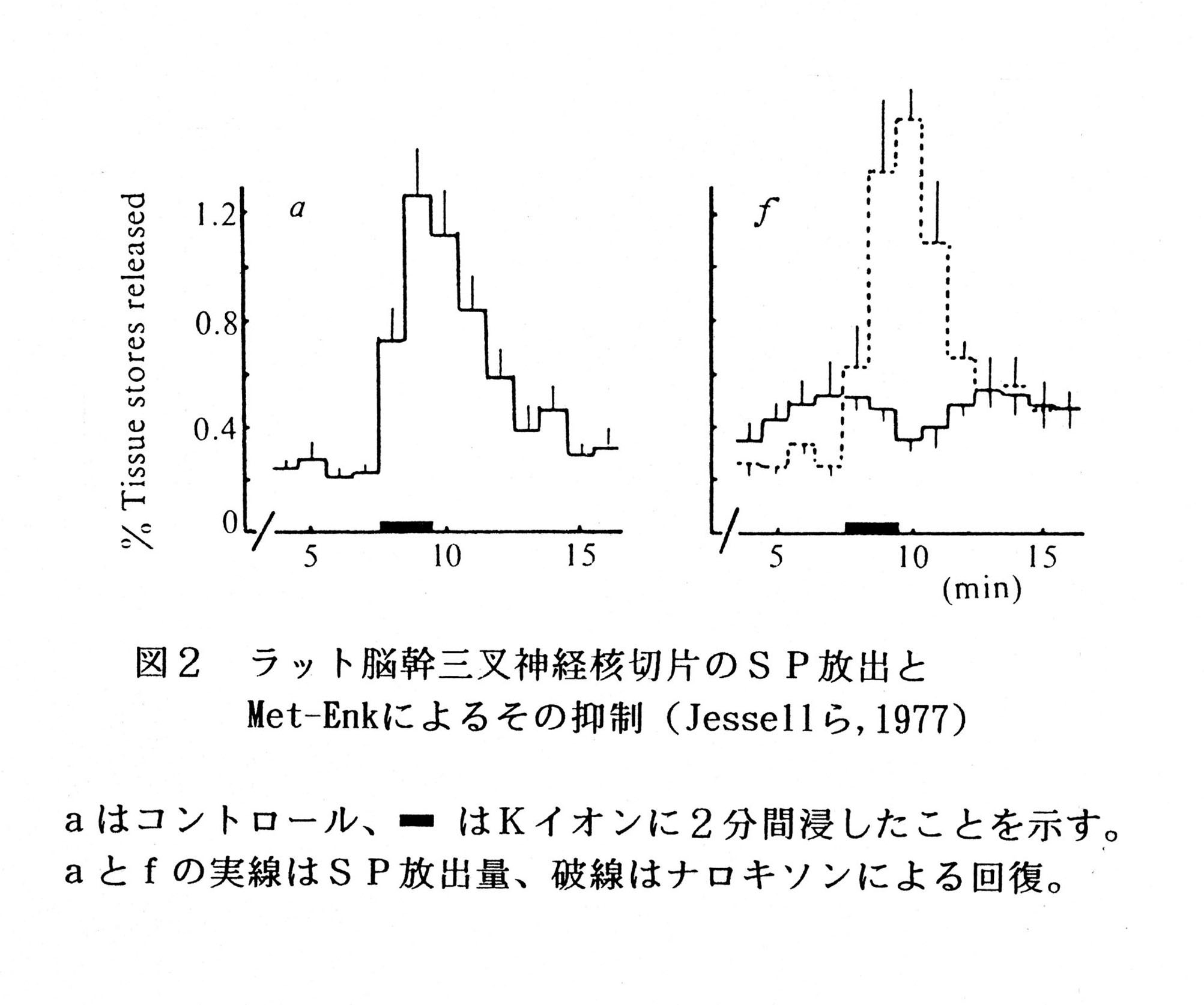
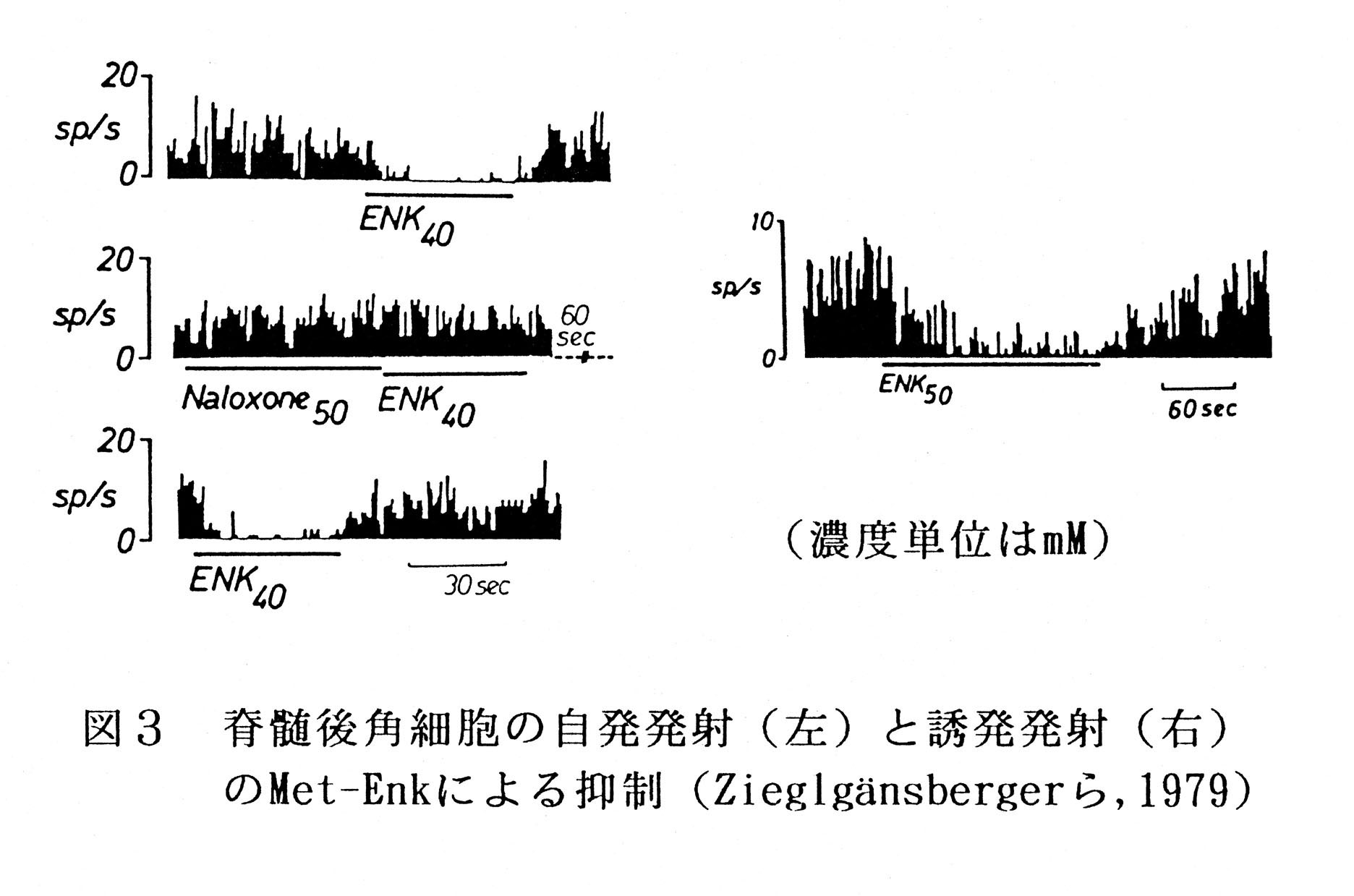
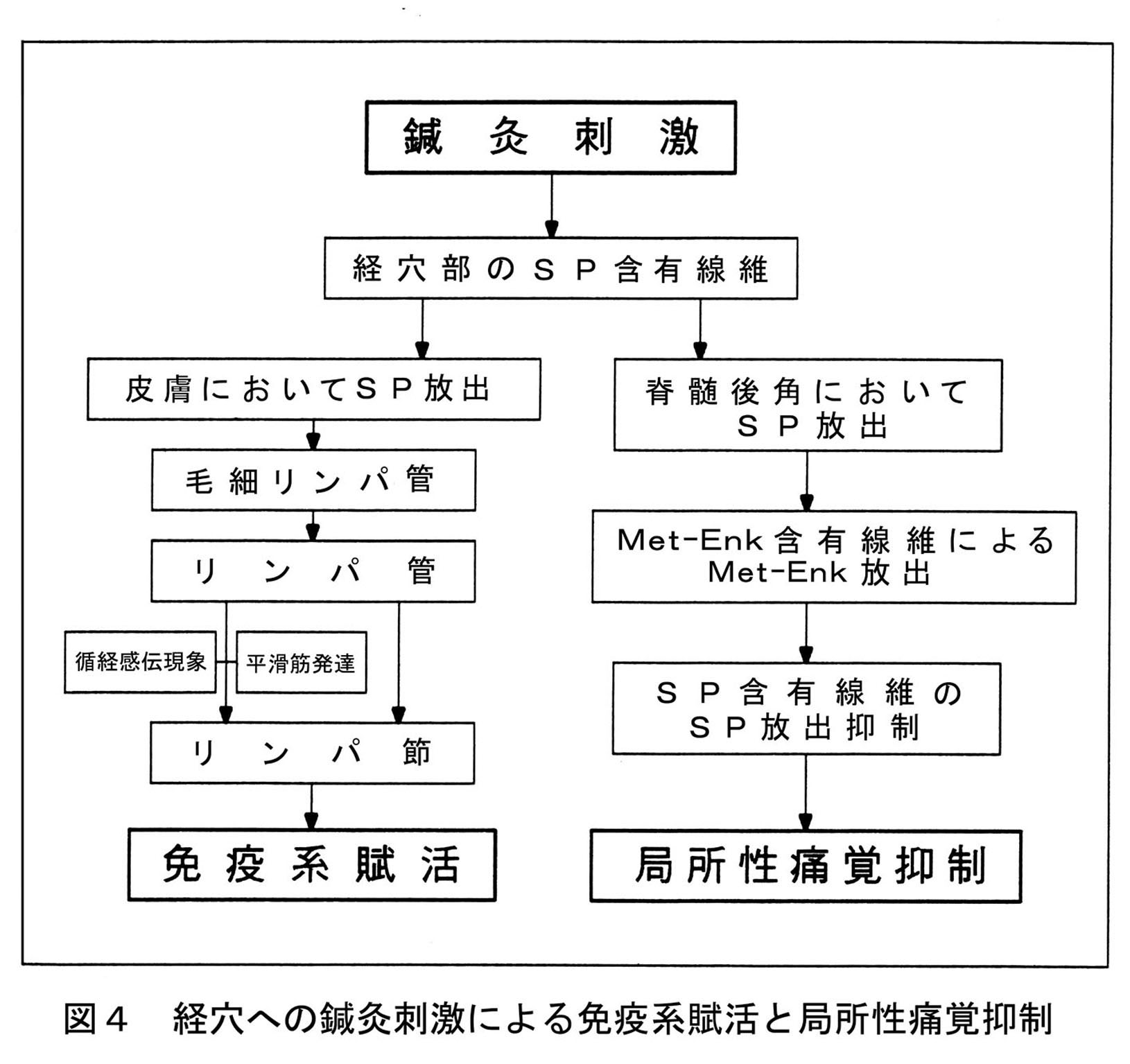
|
1) |
S.katoh et a1.:Ultrastructural Localization
of Immunolabeled Substance P and Methionine-Enkephalin-Octapeptide in the
Surface Layer of the Dorsal Horn of Rat Spinal Cord. Cell Tissue Research
253;55~60.(1988) |
| 2) |
L.Bonfanti et al.:Distribution of Five
Peptides,Three General Neuroendcrine
Markers,and Two Synaptic-Vesicle-Associated Proteins in
the Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglia of the Adu1t and Newborn
Dog:An Immunocytochemical Study. The American Journal of
Anatomy l9l;54~166.(1991) |
| 3) |
M.Kawata et al.:Brain Natriuretic Peptide in the Porcine Spinal Cord:An lmmunohistochemical Investigation of lts
Localization and the Comparison with Atrial Natriuretic Peptide,Substance P,Ca1citonin Gene-Related Peptide,
and Enkephalin. Neuroscience 33(2);401~410.(1989) |
| 4) |
S.katoh et al.: Light-and Electron-Microscopic Evidence of Costoring of lmmunoreactive Enkephalins and Substance P in Dorsal Horn Neurons of Rat. Cell Tissue Research 253;297~303.(1988).
|
| 5) |
M.A.Ruda et al.: Role of Serotonin(5-HT) and Enkephalin (Enk) in Trigeminal and Spinal Pain Pathways. Journal of Dental Research 62:691.(1983) |
| 6) |
K.K.Sumal et al.: Enkephalin-Containing Neurons in Substantia Gelatinosa of Spina1 Trigeminal Complex: Ultrastructure and Synaptic lnteraction with Primary Sensory Afferents. Brain Research 248:223~236.(1982) |
| 7) |
T.L.Yaksh et al.: Survey of Distribution of Substance P, Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide, Cholecystokinin, Neurotensin, Met-Enkepha1in, Bombesin and PHl in the Spinal Cord of Cat, Dog, SIoth and Monky. Peptides 9:357~372.(1988) |
| 8) |
T.M.Jessell et al.: Opiate Analgesicis lnhibit Substance P Release from Rat Trigeminal Nucleus. Nature 268(11);549~551,(1977)
|
| 9) |
W.Zieglgänsberger et al.: The Effects of Methionin-and Leucine-Enkephain on Spinal Neurones of the Cat. Brain Research l67;53~64.(1979) |
| 10) |
遠山正彌ほか.:化学的神経機能解剖学,397~415,第1版,厚生社,大阪.(1987) |
| 11) |
J.Tang et al.: The Effect of Peptidase lnhibitors on the Release of Met5-Enk-Arg6-Phe7(YGGFMRF) and
Met5-EnkephalIn (YGGFM) from Spinal Cord lnduced by Substance P in
Vivo. Life Science 33(Sup.1);121~124.(1983) |
| 12) |
H.M.Chang et al.: Sufentanil, Morphine, Met-Enkephalin, and K-Agonist(U-50,488H) lnhibit Substance P Release from Primary Sensory Neuron: A Model for Presynaptic Spinal Opioid Actions. Anesthesiology 70;672~677.(1989) |
| 13) |
F.Cesselin et al.: Segmental Release of Met-Enkephalin-Like Material form the Spinal Cord of Rats, Elicited by Noxious Thermal Stimuli. Brain Research 484;71~77.(1989)
|
| 14) |
M.L.De Ceballos et al.: lncreased [Met]Enkephalin and Decreased Substance P in Spinal Cord Following Thermal lnjury to One Limb. Neuroscience 36(3);731~736.(1990) |
| 15) |
花岡一雄ほか:わかりやすい神経系の話”痛みの伝導系”を探る,60~64,第2版,メディカルトリピューン,東京.(1988)
|
| 16) |
遠山正彌ほか.:化学的神経機能解剖学,395~397,第1版,厚生社,大阪.(1987) |
|
17) |
山田鑑照ほか: ヒト合谷相当部におけるSubstance-P陽性線雜とリンパ系の関連について,全日本鍼灸学会雑誌,44(2);49~154. (1994) |
| 18) |
山田鑑照ほか:経穴への鍼灸剰激がリンパ管を介して免疫系を賦活する機序について,医道の日本53(12);14~21,横須賀.(1994)
|
| 19) |
山田鑑照ほか.: 循経感伝現象がリンパ管において発現する機序について,医道の日本 54(3);22~27,横須賀.(1995) |